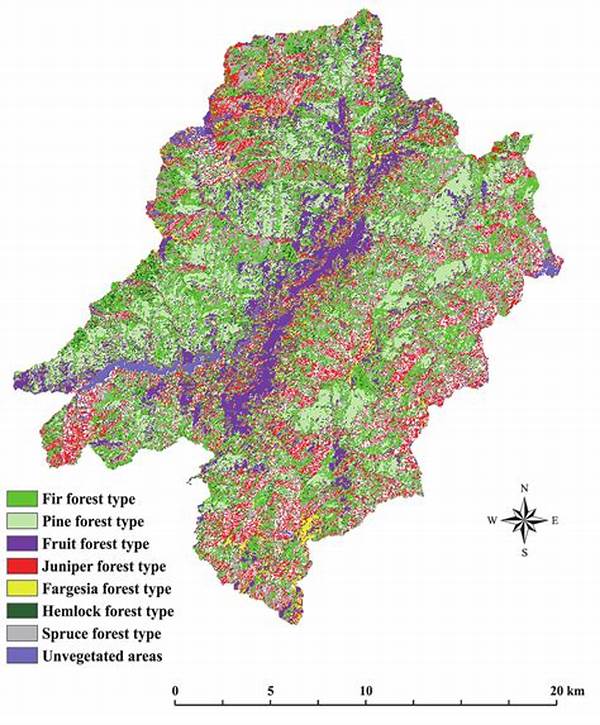
In our rapidly changing world, understanding and preserving the biodiversity of forests is more crucial than ever. One effective method for achieving this is through hue classification in forests. By leveraging color data, we can uncover critical insights about forest health and composition. The utilization of hue classification transforms conservation efforts, providing precise, actionable data for managing natural resources. Stay with us as we delve into the significance, methodologies, and benefits of hue classification in forests, and discover why it should be at the forefront of environmental strategies.
Read Now : Plant Life Color Diversity
The Importance of Hue Classification in Forests
Hue classification in forests is not just a technological advancement; it is a necessity. With deforestation and climate change posing significant threats to natural habitats, it is imperative to incorporate advanced methods for monitoring and conservation. Hue classification allows scientists to decode the intricate tapestry of forest colors, which are indicators of species diversity, health, and ecosystem dynamics. This approach can swiftly identify areas of concern and facilitate targeted conservation efforts. By implementing hue classification, forests can be monitored more effectively, ensuring their preservation for future generations. The question then arises: why shouldn’t we capitalize on this powerful tool to protect the lungs of our planet?
Moreover, hue classification in forests acts as a beacon of innovation, integrating technology with ecology. It harnesses satellite imagery and drone technology, processing vast amounts of data into coherent insights. This symbiosis of technology and nature paves the way towards sustainable forest management, offering a cutting-edge solution to centuries-old environmental challenges. It provides clarity where there was once ambiguity, transforming the way we interact with nature and encouraging a deeper appreciation for the complexity of forest ecosystems.
Finally, hue classification in forests is a proactive measure in conservation biology. As the adage goes, prevention is better than cure. By identifying and addressing issues before they escalate, hue classification enables stakeholders to make informed decisions, ensuring the long-term health and sustainability of forests. In an era where reactive solutions often fall short, this approach offers hope and clarity, empowering conservationists with the tools needed to safeguard our planet’s precious resources.
Methods for Implementing Hue Classification in Forests
1. Satellite Imagery: Utilizing high-resolution satellite images, hue classification in forests provides an expansive view, enabling the detection of changes and gradations in forest colors with pinpoint accuracy.
2. Drone Technology: Drones equipped with specialized cameras fly over forest canopies, capturing color data that contributes to hue classification in forests, assessing health and biodiversity efficiently.
3. Machine Learning Algorithms: Advanced algorithms process and analyze the substantial data from both drones and satellites, enabling precise hue classification in forests by identifying patterns and anomalies.
4. Ground Truthing: This vital step involves on-site verification of satellite and drone data, ensuring the accuracy of hue classification in forests by correlating digital information with real-world conditions.
5. Spectral Analysis: By examining various wavelengths reflected by forest elements, spectral analysis sharpens the process of hue classification in forests, offering detailed insights into species composition and health.
Benefits of Hue Classification in Forests
Hue classification in forests offers myriad benefits, revolutionizing how we manage and understand these vital ecosystems. Firstly, it elevates efficiency in conservation efforts. By providing comprehensive data on forest health, it allows conservationists to focus resources on areas that need immediate attention, thus optimizing both time and funds. Secondly, it empowers local and indigenous communities by involving them in monitoring efforts, raising awareness and attributing a sense of stewardship over their natural surroundings.
Furthermore, this approach is instrumental in mitigating climate change effects. By precisely mapping and monitoring deforestation rates and changes in forest composition, hue classification in forests aids in curtailing habitat loss, thereby preserving biodiversity. As biodiversity acts as a buffer against climate fluctuations, preserving it through hue classification indirectly supports global climate stabilization efforts.
Lastly, hue classification in forests serves as an essential educational tool. By demystifying the complex interactions within forest ecosystems, it fosters a greater understanding and appreciation of nature among the public. Educating people about the importance of forest health encourages more sustainable behavior and advocacy for conservation initiatives. The implementation of hue classification in forests, therefore, is not just a technical exercise, but a catalyst for broader ecological awareness and action.
The Future of Hue Classification in Forests
1. Technological Innovation: Future advancements in technology will continue to refine hue classification in forests, making the process even more precise and accessible.
2. Policy Integration: There is potential for hue classification data to be integrated into policy-making, enhancing forest management and conservation strategies.
3. Global Collaboration: As hue classification techniques evolve, international partnerships could facilitate the sharing of data and resources, maximizing its global impact.
4. Real-Time Monitoring: Continuous advancements could lead to real-time monitoring capabilities, providing immediate data updates and facilitating rapid response to changes in forest ecosystems.
5. Public Engagement: As public interest in sustainability grows, hue classification could become a topic of broader interest, inspiring citizen science projects and community involvement in forest conservation.
Read Now : Simple And Cozy Scandinavian Interiors
6. Cost Reduction: As the technology becomes more widespread, the costs associated with hue classification in forests are likely to decrease, making it a viable option for conservation organizations with limited budgets.
7. Broader Applications: Beyond forests, hue classification techniques could be adapted for use in other ecosystems, broadening the scope and impact of this innovative approach.
8. Interdisciplinary Research: Collaborative research across fields such as ecology, computer science, and geospatial studies could further enhance the effectiveness of hue classification in forests.
9. Customized Solutions: Tailored hue classification models could be developed for specific forest types or conservation objectives, increasing their relevance and impact.
10. Cultural Sensitivity: Implementing hue classification in a way that respects and involves local and indigenous knowledge systems could enrich the data and foster community support for conservation initiatives.
Challenges and Considerations in Hue Classification
While hue classification in forests is an innovative tool, it comes with its own set of challenges and considerations. Firstly, the accuracy of color data relies heavily on the quality of imagery and sensor technology. Any limitations or malfunctions in these tools could potentially distort the hue classification results. Therefore, consistent investment in state-of-the-art technology is essential to maintain the integrity of the data.
Secondly, implementing hue classification requires collaboration across multiple disciplines and stakeholders, which might lead to logistical and bureaucratic challenges. Coordinating efforts between government bodies, research institutions, and local communities necessitates clear communication and alignment of objectives, ensuring that hue classification efforts are not fragmented or duplicated unnecessarily.
Moreover, there is an ethical dimension to consider when employing hue classification in forests. While the technology provides valuable insights, there must be a careful balance between technological intervention and respect for the natural rhythms and dynamics of forest ecosystems. Ensuring that the data collected is used ethically and transparently is paramount, safeguarding against misuse or misrepresentation of information.
Overcoming Barriers to Adoption
To fully harness the potential of hue classification in forests, barriers to its adoption must be addressed. One of the primary hurdles is the need for education and training. Both technical experts and local communities must be equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary to interpret hue classification data effectively. Initiatives aimed at capacity building and knowledge sharing will facilitate the widespread adoption of this technology.
Financial constraints also pose significant challenges, particularly for conservation organizations operating on limited budgets. Government grants, international aid, and private sector partnerships can provide the funding necessary to implement hue classification projects. Additionally, proving the long-term cost efficiency of this technology by highlighting its ability to optimize resource allocation will support the case for investment.
Finally, fostering a culture of innovation and collaboration is essential. Breaking down silos between different sectors and encouraging interdisciplinary research will drive the evolution and enhancement of hue classification methodologies. As more success stories emerge, confidence in hue classification in forests will grow, prompting broader acceptance and integration into environmental conservation frameworks.
Advancing Conservation through Hue Classification
Hue classification in forests represents a transformative approach to environmental conservation. By enabling precise monitoring and analysis of forest ecosystems, it offers an unmatched ability to identify and address ecological challenges. As we continue to refine and adopt this technology, the impact on forest conservation efforts will be profound and far-reaching.
Empowering conservationists with comprehensive data, hue classification facilitates informed decision-making and strategic resource allocation. This is particularly important in an era where environmental issues must be tackled proactively rather than reactively. By ensuring timely intervention, hue classification reduces the risk of irreversible damage to forest ecosystems, preserving biodiversity and supporting climate resilience.
Ultimately, the integration of hue classification into conservation efforts highlights the potential of technology to drive positive environmental change. As communities and policymakers around the globe recognize the importance of maintaining healthy forests, hue classification will serve as a crucial ally, guiding efforts to protect and preserve these vital ecosystems for future generations. By embracing this innovative approach, we are taking a significant step towards a more sustainable and harmonious relationship with our natural world.